Choosing the right ammonia nitrogen sensor can be challenging. Many options exist in the market. Each design caters to specific needs and applications. Understanding the factors involved in selection is crucial.
Different ammonia nitrogen sensors have unique features. Some are more sensitive than others. Their cost, accuracy, and maintenance requirements vary greatly. It’s important to determine your specific requirements before making a decision. For instance, what environment will you use the sensor in? This can impact its effectiveness.
You may find yourself overwhelmed by choices. This process involves reflection. Consider the purpose of your sensor. Will it be for wastewater treatment, agriculture, or another field? Each application may require a different type of ammonia nitrogen sensor. The right choice ensures better performance and reliability. Emphasizing these points helps clarify what you truly need.

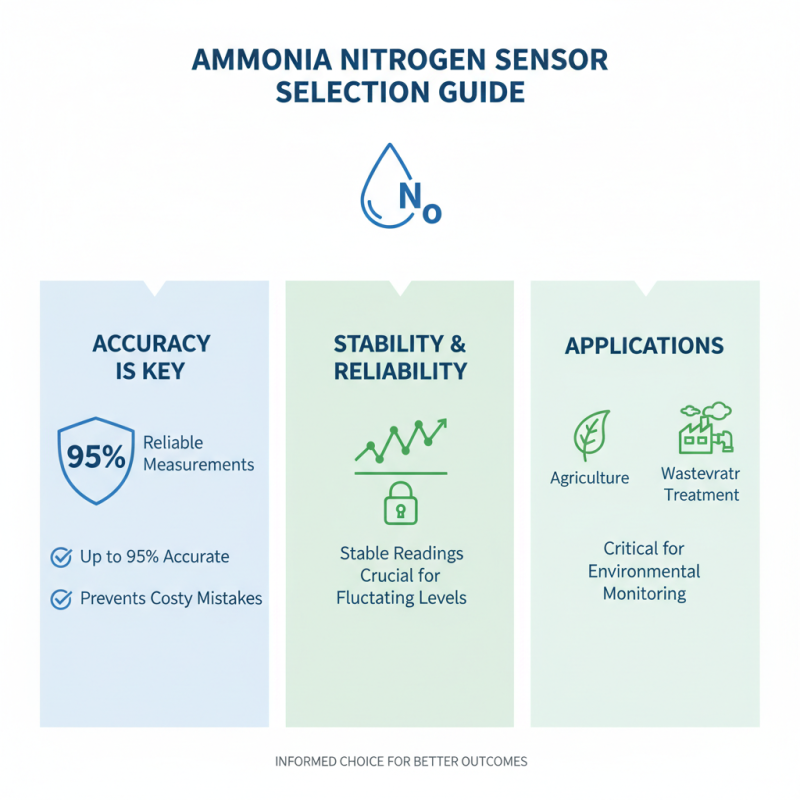
When selecting an ammonia nitrogen sensor, various factors merit careful consideration. Accuracy is paramount. The best sensors achieve an accuracy level of about 95%, reflecting reliable measurements. This is crucial for environments where ammonia levels fluctuate frequently. A sensor that provides stable readings can help prevent costly mistakes in agriculture or wastewater treatment.
Another key aspect is the sensor's response time. Many sensors boast response times under 1 minute. This quick feedback allows for timely action, which is vital in critical applications. However, some models may lag, potentially causing issues. Understanding this aspect can help in avoiding delays in response.
Durability is also important. Some sensors are designed to last years in harsh conditions. However, others may require frequent replacements or calibration. This raises the question of cost versus longevity. Monthly maintenance can quickly add up, offsetting any initial savings. Choosing the right ammonia nitrogen sensor involves weighing these practical considerations carefully.
When selecting an ammonia nitrogen sensor, understanding the types available is crucial. Three main categories dominate the market: optical sensors, electrochemical sensors, and solid-state sensors. Optical sensors use an advanced method to detect ammonia levels through light absorption. They can provide fast and precise readings, typically within 30 seconds. However, they can be expensive and may not be suitable for all environments.
Electrochemical sensors are widely recognized for their responsiveness and affordability. According to a recent industry report, these sensors can detect ammonia concentrations as low as 0.1 ppm. They are commonly used in both industrial and agricultural settings. Yet, they can have a limited lifespan and might require regular calibration. This can lead to potential inaccuracies over time, especially in harsh conditions.
Solid-state sensors offer robustness in various applications. They use semiconductor technology, making them durable and resistant to environmental factors. But a study indicates that their sensitivity can decline over time, necessitating careful assessment of performance. Choosing the right sensor requires weighing the benefits and limitations of each type. Understanding these factors will help tailor solutions to specific monitoring needs.
When selecting an ammonia nitrogen sensor, understanding key specifications is essential. Focus on detection limits. A low limit indicates better sensitivity, which is crucial for precise measurements. Accuracy is another critical metric. It tells you how close the sensor's readings are to the actual ammonia level. For many, achieving both sensitivity and accuracy can be a challenge.
Consider the sensor's response time as well. A quick response helps monitor changes effectively. If the sensor lags, it may not give you timely data. Calibration requirements also matter. Some sensors need frequent calibration, while others are more stable. This aspect can impact operational efficiency and costs.
Think about the environment too. Different sensor types may perform better under specific conditions. For example, high humidity or temperature fluctuations can affect performance. It's essential to reflect on these factors before making a choice. Sometimes, the most advanced model isn’t the best for your situation. Balancing features with actual needs can lead to better decisions.
Ammonia nitrogen sensors play a crucial role in various industries, including agriculture and wastewater management. These sensors are designed to detect ammonia levels accurately, which is vital for regulatory compliance and environmental protection. In agriculture, controlling ammonia levels can enhance crop yield. Studies indicate that approximately 40% of nitrogen applied in farming is lost as ammonia gas. This emphasizes the need for effective monitoring solutions.
In wastewater treatment, ammonia sensors are essential. They help ensure that effluent meets environmental standards. Research shows that elevated ammonia levels can harm aquatic life. Preserving ecosystem health is a priority. As a result, sensors must be reliable and responsive to meet stringent requirements. Sensor calibration is also critical. Inconsistent readings can lead to poor decision-making. Users should consider factors such as the sensor's response time and maintenance needs. Some sensors require frequent recalibration, which can be a burden.
Different applications demand unique specifications. For example, industrial emissions monitoring requires sensors that can withstand harsh conditions. On the other hand, agricultural applications might focus on portability and ease of use. Identifying the right sensor requires careful evaluation of these factors. Users should reflect on their specific needs, as selecting a sensor based solely on price could lead to inadequate performance.

When selecting an ammonia nitrogen sensor, maintenance and calibration are crucial. Regular upkeep ensures that the sensor delivers accurate readings. Over time, environmental factors like temperature and humidity can affect performance. Regularly check for any signs of dirt or corrosion on the sensor surface. Keeping it clean is vital for proper functioning.
Calibration processes should be performed periodically. This adjustment compensates for any drift in sensor performance. Use reliable calibration solutions to match the sensor's range. Calibration may seem straightforward, yet many overlook this step. Over time, an uncalibrated sensor may provide misleading results. Even small discrepancies can lead to significant errors in monitoring ammonia levels.
Consider creating a maintenance schedule. This plan can help ensure regular checks and calibrations are not missed. Document every maintenance activity. This record can reveal patterns in sensor performance and highlight areas for improvement. Reflecting on these aspects can significantly enhance the reliability of your ammonia nitrogen sensor.