Safeguarding Our Waters: Key Parameters to Monitor in Wastewater Treatment Effluent
In the process of wastewater treatment, monitoring effluents is a key link to protect the ecological environment and public health. By monitoring specific parameters, we can timely grasp the effect of wastewater treatment and ensure that the quality of the discharged water meets relevant standards. The following are the key effluent parameters that should be monitored in wastewater treatment:

Physical Parameters
- Temperature: Water temperature affects the content of dissolved oxygen in water and the living environment of aquatic organisms. Excessively high or low water temperature may have adverse effects on the aquatic ecosystem.
- TotalSuspended Solids (TSS): Suspended solids refer to solid particles suspended in water. Excessive content will make the water turbid, reduce the transparency of the water body, and affect the photosynthesis of aquatic plants. At the same time, suspended solids may also deposit at the bottom of the water body, destroying the habitat of aquatic organisms.
Chemical Parameters
- pH Value: The pH value reflects the acidity and alkalinity of water. The pH value of normal water bodies is usually between 6 and 9. If the pH value of the effluent exceeds this range, it will destroy the acid-base balance of the water body, have toxic effects on aquatic organisms, and corrode facilities such as drainage pipes.
- Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) and Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD): COD refers to the amount of oxygen consumed by oxidizing organic matter in water with a strong oxidant under certain conditions; BOD refers to the amount of oxygen consumed by microorganisms decomposing organic matter in water under aerobic conditions. These two parameters are important indicators to measure the content of organic matter in water. The higher their values, the more organic matter in the water, and the more serious the pollution of the water body.
- Dissolved Oxygen (DO): Dissolved oxygen refers to the oxygen dissolved in water, which is essential for the survival of aquatic organisms. If the dissolved oxygen content in the effluent is too low, it will lead to hypoxia in the water body, cause the death of aquatic organisms, and make the water body smelly.
- Nitrogen and Phosphorus: Nitrogen and phosphorus are essential nutrients for plant growth. However, if their contents in water are too high, they will lead to eutrophication of the water body, causing a large number of algae to reproduce. The decomposition of dead algae will consume a lot of dissolved oxygen, further deteriorating the water environment, and even leading to phenomena such as "water blooms" or "red tides".
- Heavy Metals: Heavy metals such as mercury, cadmium, lead, and chromium are highly toxic, difficult to degrade in the environment, and will accumulate in organisms, causing serious harm to human health and the ecosystem.
Biological Parameters
- Total Bacterial Count and Coliform Count: These microbial indicators reflect the sanitary condition of the water body. If the total number of bacteria and coliforms in the effluent is too high, it indicates that the water body may be polluted by feces and other pollutants, and there is a risk of spreading diseases.
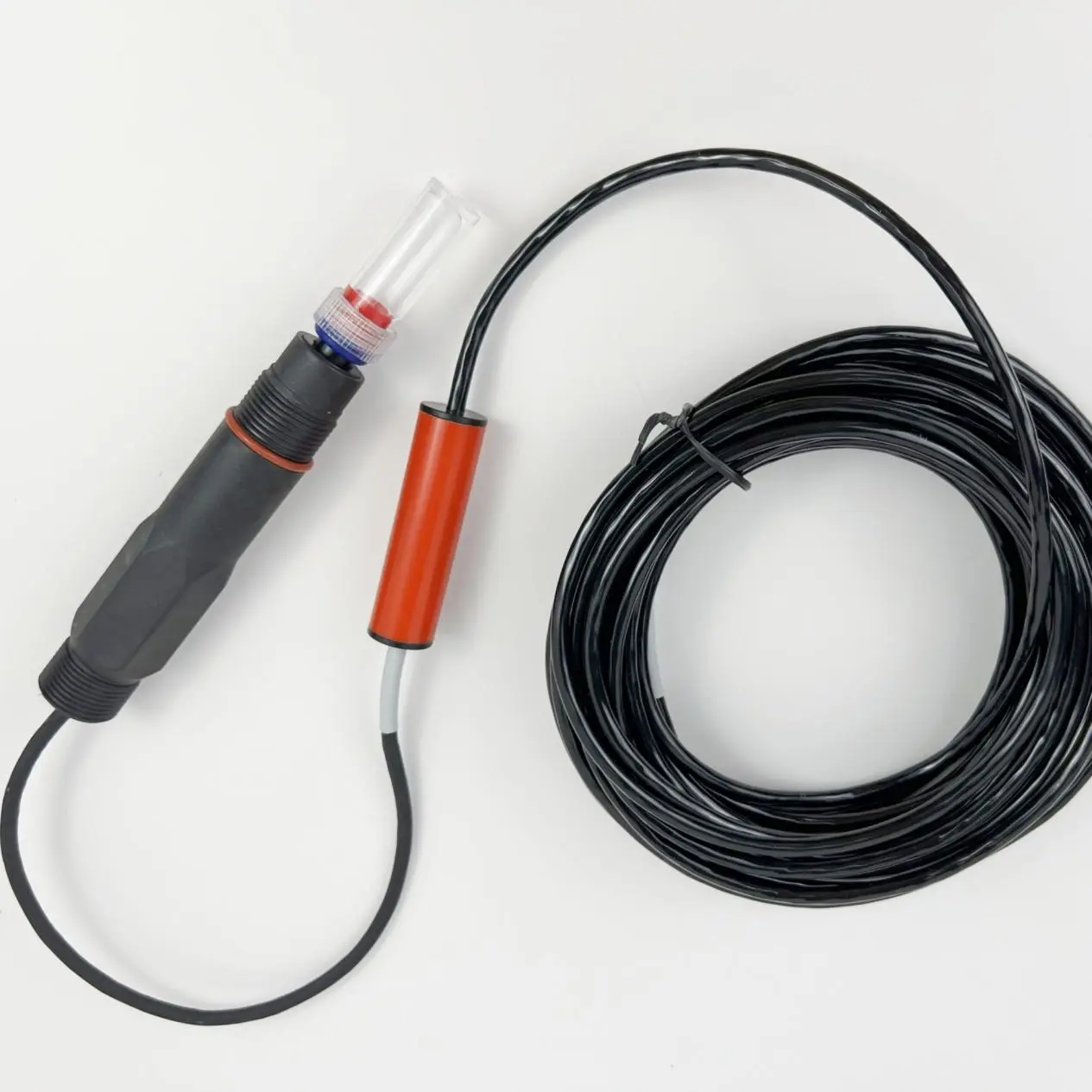
Regular monitoring of these parameters of wastewater treatment effluents can timely detect problems and take corresponding treatment measures, thereby effectively reducing environmental pollution and protecting ecological balance and human health. The Cod Sensor of LUMINSENS, such as the models LMS - COD100H and LMS - COD100L, adopts the ultraviolet absorption method, requires no reagents, causes no pollution, and can accurately measure parameters such as COD, TOC, BOD, turbidity, and temperature. It has advantages such as automatic compensation for turbidity interference, a self - cleaning brush to prevent biological adhesion, simple operation and maintenance, fast response (on the order of tens of seconds), high stability, and no interference from chloride ions. It provides a reliable and efficient solution for monitoring the parameters of effluents in wastewater treatment, helping to safeguard the quality of the water environment.